Physical education test
Option number 1
1. Physical culture means:
A) part of the culture of society and man;
B) the process of developing physical abilities;
C) a type of education aimed at teaching movements and developing physical qualities;
D) development of natural forces of nature and education of hygienic qualities.
2. The result of physical training is:
A) physical development;
B) physical perfection;
C) physical fitness;
D) the ability to correctly perform motor actions.
3. When did Russia first take part in the Olympic Games?
A) 1908 in London;
B) 1912 in Stockholm;
B) 1952 in Helsinki;
D) 1928 in Amsterdam.
4. Running with stops and change of direction on a signal predominantly contributes to the formation of:
A) coordination of movements;
B) movement techniques;
C) speed of reaction;
D) speed strength.
5. It is best to take sunbathing:
A) from 12 to 16 noon;
B) before 12 and after 16 noon;
B) at any time of the day, subject to the necessary precautions;
D) from 10 to 14 hours.
6. Cyclic sports include ...:
A) wrestling, boxing, fencing;
B) basketball, volleyball, football;
B) walking, running, cross-country skiing, swimming;
D) throwing a ball, disc, hammer.
7. Where and when were the first modern Olympic Games held?
A) 1516 in Germany;
B) 1850 in England;
C) 1896 in Greece;
D) 1869 in France.
8. The main cause of poor posture is:
A) sedentary lifestyle;
B) weakness of the back muscles;
B) the habit of carrying the bag on one shoulder;
D) long stay in a sitting position at a desk.
9. What is the name of the first Russian Olympic champion:
A) Nikolay Panin-Kolomenkin (figure skating);
B) Ivan Poddubny (wrestling);
C) Sergey Eliseev (weightlifting);
D) Anatoly Reshetnikov (athletics)
10. The document representing all aspects of the organization of the competition is:
A) competition calendar;
B) regulations on competitions;
C) competition rules;
D) competition program.
11. Prevention of posture disorders is carried out when:
A) speed exercises;
B) exercises "for flexibility";
B) strength training;
D) endurance exercises.
12. Which organization is involved in the preparation and conduct of the Olympic Games?
13. In what sport did the Far East woman Yulia Chepalova win the gold medal at the 17th Olympic Games?
A) downhill;
B) speed skating sprint;
B) freestyle;
D) cross-country skiing.
14 The position of the student, in which the legs bent at the knees are pulled up by the hands to
chest and hands grab the knees, in gymnastics it is designated as
__________________________________________________________________
15 Motor actions that are aimed at solving problems of physical education,
formed and organized according to its laws, called
1-a, 2-c, 3-a, 4-c, 5-b, 14-grouping, 15-physical exercise.
Physical education test
Option number 2
1 .What defines safety engineering?
A) knowledge skills of physical exercises without injuries;
B) a set of measures aimed at teaching the rules of behavior, the rules of insurance and self-insurance, the provision of first aid;
C) correct exercise;
D) organization and conduct of educational and extracurricular activities in accordance with hygienic requirements.
2. Choose the correct sequence of actions to provide first aid for fainting:
A) put the victim in a cool place, fan with a towel, give an abundant warm drink;
B) a cold compress on the head, rest, the legs are given an elevated position;
B) a warm compress on the head, unfasten the clothes that are restricting breathing, shallow massage of the neck area, cold drink;
D) give the victim a horizontal position, provide an influx of fresh air, wipe his face with cold water, let the ammonia smell .
3. What definition does not apply to the main properties of muscles?
A) stretching;
B) reduction;
B) elasticity;
D) constancy of state
4. The meaning of physical culture as a component of the culture of society is:
A) strengthening of health and education of physical qualities of people;
B) teaching motor actions and improving performance;
C) in improving the natural, physical properties of people;
D) motor activity organized in a certain way.
5. What test does not determine the physical quality of endurance?
A) 6 minutes run;
B) running 100 meters;
C) cross-country skiing for 3 kilometers;
D) swimming 800 meters.
6. What is the length of the marathon distance at the Olympic Games?
A) 42 km 195 m;
B) 32 km 195 m;
B) 50 km 195 m;
D) 45 km 195 m.
7. In which city will the 2008 Summer Olympics be held?
A) Grenoble (France);
B) Tokyo (Japan);
B) Beijing (China);
D) St. Louis (USA)
8. Indicate what exercises are typical for the final part of the physical education lesson?
9. How are flexibility exercises dosed, that is, how many movements should be done in
one episode? Flexibility exercises are performed ...
A) 8-16 cycles of movements in a series;
B) until the range of motion begins to increase;
B) before the onset of pain;
D) 10 cycles in 4 series.
10. Who came up with the proposal to revive the Olympic Games?
A) Jean Jacques Rousseau;
B) Juan Antonio Samaranch;
C) Pierre de Coubertin;
D) Jan Amos Kamensky.
11. What is adaptation?
A) the process of adaptation of the body to changing environmental conditions;
B) alternation of load and rest during the training process;
C) the recovery process;
D) a system for increasing the efficiency of the functioning of the competition system and the training system.
12. What are the normal resting heart rates of a healthy untrained adult?
A) 60-80;
B) 70-90;
Answering questions 13-15, you need to independently choose a word that, completing the statement, forms a true statement. Enter the selected word in the assignment form.
13 A jump from an apparatus in gymnastics is denoted as ______________
1. The first official participation of Russia in the Olympic Games happened at the Games ...
a. II Olympiad in Paris (1900).
b. IV London Olympics (1908).
v. V Olympiad in Stockholm (1912).
the VII Olympiad in Antwerp (1920).
2. For the first time, the Olympic oath of athletes to fight honestly sounded in…. year.
a. 1912 b. 1920 c. 1952 1960
3. The International Olympic Committee has decided to hold the Winter Olympic Games in…. year.
a. 1920 b. 1922 c. 1924 1925
4. In the Winter Olympic Games, the USSR made his debut in ...
a. 1952 at the VI Games in Oslo, Norway.
b. 1952 at the XV Games in Helsinki, Finland.
v. 1956 at the VII Games in Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy.
1960 at the VIII Games in Squaw Valley, USA.
5. The emergence and initial formation of physical education as a social phenomenon was determined ...
a. the law of survival.
b. material status.
v. social necessity.
d. personal interest.
6. Complete the definition by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The pedagogical process aimed at teaching movements, fostering physical qualities, mastering special physical culture knowledge and fostering moral and volitional qualities is usually called physical ...
7. Complete the definition by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The process of formation and change of biological forms and functions of the organism, taking place under the influence of the living conditions of upbringing is called physical ...
8. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The level of physical development and fitness of a person that meets the requirements of life is usually designated as physical ...
9. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The most significant result of the full functioning of physical culture in society is associated with the concept of "physical ..."
10. The need to prepare people for life, work, and other necessary types of activity historically conditioned the emergence of ...
a. physical culture.
b. physical education.
v. physical perfection.
of sports.
11. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The state of the body, characterized by perfect self-regulation of organs and systems, a harmonious combination of physical, moral and social well-being is called ...
12. The reaction of the cardiovascular system is assessed as bad if the difference in heart rate between lying and standing is ...
a. less than 12 bpm
b. from 12 to 18 bpm
v. from 19 to 25 bpm
more than 25 beats / min.
13. The state of health is due to ...
a. way of life.
b. lack of disease.
v. the level of health care.
d. reserve capacities of the organism.
14. The health-improving effect in the classroom of adolescent students is achieved with the help of ...
a. conducting classes on a regular, enlarged and reduced area.
b. changes in the number of repetitions of the same exercise.
v. aerobic exercises of medium and high intensity.
d. exercise with an intensity above the threshold of anaerobic metabolism.
15. The most important component of a healthy lifestyle is ...
a. motor mode.
b. balanced diet.
v. personal and public hygiene.
hardening of the body.
16. Which of the presented definitions is not formulated correctly?
a. Physical perfection is the optimal measure of all-round
physical fitness and harmonious physical
development that meets the requirements of society.
b. Physically perfect can be considered a person capable of
“Cope” with the Presidential Test standards.
v. Physically perfect can be recognized as a person, physical
the state of which allows you to implement any function,
which society will demand of him.
d. Physical perfection is a process of change
morpho-functional properties of the body throughout
individual life.
17. The health-improving value of physical exercise determines them ...
a. the form. b. content. v. technique. d. hygiene.
18. The process aimed at improving the motor abilities necessary in life is designated as ...
a. physical training.
b. physical education.
v. physical perfection.
19. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The position of the student when his shoulders are above the fulcrum is called ...
20. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The position of those engaged in bent legs is called ...
21. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
Free movement of a body about the axis of rotation is called ...
22. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
A quick transition from stop to vis is called ...
23. The basis of the methodology for the education of physical qualities is ...
a. age adequacy of the load.
b. training in motor actions.
v. exercise.
d. a gradual increase in the force of impact.
24. The relationship between the volume and intensity of physical activity is characterized by ...
a. an increase in the body's responses.
b. inversely proportional relationship.
v. indicators of the pace and speed of movements.
d. by directly proportional dependence.
25. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The impact on the human body of an external factor that violates the structure and integrity of tissues and the normal course of physiological processes is called ...
26. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
It is customary to call a temporary decrease in working capacity ...
27. The method of repeated exercise with non-limit weights when performing actions performed to failure is used in education ...
a. strength.
b. you were fast.
v. endurance.
speed power.
28. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The maximum range of motion achieved by the application of both internal and external forces characterizes…. flexibility.
29. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The method of organizing the activities of students, when everyone performs the same task, is called ...
30. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The method of organizing the activities of students, providing for the simultaneous execution of several groups of different tasks, is called ...
31. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The method of organizing the activities of students, providing for the sequential execution of a series of tasks dosed individually on the basis of the maximum test, is called ...
32. The basis of the "continuity" of physical education is ...
a. lack of rest intervals.
b. the interaction of the effects of exercise.
v. a combination of health-improving and developmental activities.
d. a variety of forms of employment.
33. In the process of teaching motor actions, the methods of holistic or dismembered exercise are used. The choice of method depends on ...
a. teacher preferences.
b. the number of elements that make up a motor action.
v. the possibility of dismemberment of the motor action.
d. the complexity of the motor action.
34. Indicate the sequence of problem solving in the process of teaching motional actions.
1. Anchoring. 3. Learning.
2. Familiarization. 4. Improvement.
a. 1, 2, 3, 4.b. 2, 3, 1, 4.c. 3, 2, 4, 1.d. 4, 3, 2, 1.
35. Complexes of genetically determined biological properties of the human body, due to which physical activity is possible, are usually called ...
a. physical qualities.
b. muscle tension.
v. functional systems.
d. coordination abilities.
37. The method of uniform continuous exercise is the most common in education ...
a. special endurance.
b. speed endurance.
v. general endurance.
d. elementary forms of endurance manifestation.
38. Exercises promoting the development of endurance are advisable to perform in ...
a. the end of the preparatory part of the lesson.
b. the beginning of the main part of the lesson.
v. in the middle of the main part of the lesson.
d. the end of the main part of the lesson.
39. Complete the statement by writing the appropriate word on the answer sheet.
The periods of ontogenesis, within which the most significant rates of development of certain human abilities are provided, especially favorable prerequisites for the formation of certain skills and abilities are called ...
40. What vitamin has a beneficial effect on the functions of the central nervous system, increases the body's resistance to adverse factors? Its deficiency leads to a decrease in mental and physical performance, and an excess leads to insomnia, headaches, and the deposition of kidney stones.
a. A. b. V. in. S. g. RR.
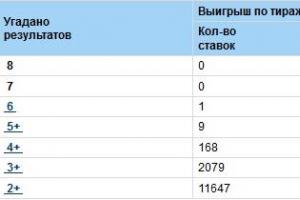
These tests help to check the knowledge of students in the subject of physical education. It will also allow you to qualitatively prepare for the Olympiad for schoolchildren in a subject or any form of control. The package contains questions and answers to these questions.
"Option 8. Questions"
Option number 8.Questions.
A) carbohydrates;
A) male sex hormones;
B) female genital organs;
B) protein substances
A) 1-2 times;
B) 10-12 times;
C) 15-20 times
4. Gymnastics.Projectile jump:
A) jump;
B) dismount;
A) keep upright;
B) tilt forward;
B) reject back
6. Basketball tactics.
A) personal protection;
B) zone protection;
B) mixed defense
7. Ski training.
A) no more than 2-3 cm;
B) not less than 5 cm
B) during the period of the games, wars stopped
A) Ancient Greece or Hellas
B) Egypt
10. What was the name in Ancient Greece pentathlon?
A) pankration
B) athletics
B) pentathlon
D) gymnastics
A) high jump
B) long jump from a place
C) triple jump
A) stepping over
B) cross-over
C) fosbury flop
D) bending over
B) four
D) eight
A) simulator;
B) stuffed balls;
B) hoops;
D) crossbar.
A) in 1956;
B) in 1960;
C) in 1952
A) tiredness
B) voltage
C) fatigue
D) overdose
A) the distance between the practitioners "In depth"
B) from the beginning of the warm-up
B) from the greetings of the teams
D) jump ball in the center circle.
A) "with a running start"
B) "stepping over"
C) "roll-over"
D) "scissors"
21.
A) "excellent";
B) "good";
C) "satisfactory";
D) "bad".
A) 80 - 70 beats / min;
B) 70 - 60 beats / min;
B) 60 - 50 beats / min;
D) 40 beats / min and below.
A) test for coordination of movements;
A) four sections: two ventricles and two atria;
A) buckwheat;
A) hiking trips;
B) compliance with the rules of hygiene;
C) sports entertainment;
D) unlimited TV viewing.
C) long running, skiing, swimming
28. The hardening of the lens of the eye is called ...
29. The ability to overcome external resistance or counteract it through muscular efforts is called….
30. A type of luge is called….
31. The impact on the human body of an external factor that violates the structure and integrity of tissue, and the normal course of physiological processes is called ... ..
32. The athletics pushing apparatus is called ... ..
33. The volleyball court separator is called ... ..
34. The uniform of a sports team is called ... ..
35. Items that protect the shins of football players and hockey players are called ... ..
View document content
"Option 8. Answers"
Option number 8. Answers.
1. Food and drinking regime. The building materials of the body are:
A) carbohydrates;
B) proteins
2. Thieves of health. Anabolic drugs contain special synthetic products:
A) male sex hormones;
B) female genital organs;
B) protein substances
3. Athletic gymnastics. The optimal weight for the simultaneous development of maximum strength, strength endurance and muscle mass is one that can be lifted:
A) 1-2 times;
B) 10-12 times;
C) 15-20 times
4. Gymnastics.Projectile jump:
A) jump;
B) dismount;
5. Cross training. When climbing a mountain, the body needs to be relative to the slope:
A) keep upright;
B) tilt forward;
B) reject back
6. Basketball tactics.Each player is responsible for the actions of a specific attacker of the opposing team:
A) personal protection;
B) zone protection;
B) mixed defense
7. Ski training.When determining stiffness, the clearance between skis connected by sliding surfaces should be:
A) no more than 2-3 cm;
B) 4-6 cm;
B) not less than 5 cm
8. Why were the ancient Olympic Games called the holidays of the world?
A) the games were distinguished by a peaceful nature
B) during the period of the games, wars stopped
C) athletes from all over the world took part in the Olympic Games
D) the Olympic Games were world famous
9. Birthplace of the ancient Olympic Games?
A) Ancient Greece or Hellas
B) Egypt
10. What was the name in Ancient Greece pentathlon?
A) pankration
B) athletics
B) pentathlon
D) gymnastics
11. Athletics. What kind of jumps is included in the rapid test program for schoolchildren?
A) high jump
B) long jump from a place
C) triple jump
12. Athletics. Indicate the incorrectly named type of high jump:
A) stepping over
B) cross-over
C) fosbury flop
D) bending over
13. Volleyball. How many replacements can you make in one batch?
B) four
At six o'clock
D) eight
14. Which of the following equipment belongs to artistic gymnastics?
A) simulator;
B) stuffed balls;
B) hoops;
D) crossbar.
15. Football. When was the first world championship held?
C) 1930.
16. When did the USSR athletes take part in the Winter Olympic Games for the first time?
A) in 1956;
B) in 1960;
C) in 1952
17.Temporary decrease in working capacity is usually called:
A) tiredness
B) voltage
C) fatigue
D) overdose
18. What is meant by the term "Distance" in gymnastics?
A) the distance between the practitioners "In depth"
B) the distance between the practitioners "along the front"
B) the distance from the one in front of the student to the one standing behind the formation
D) the distance from the first rank to the last
19. The basketball game begins….
A) from the time indicated in the schedule of games
B) from the beginning of the warm-up
B) from the greetings of the teams
D) jump ball in the center circle.
20. One of the ways of the long jump in athletics is designated as a jump ...
A) "with a running start"
B) "stepping over"
C) "roll-over"
D) "scissors"
21. An eighteen-year-old student (student) covered a distance of 2 km 700 m (2 km 200 m) in 12 minutes. The degree of his (her) physical fitness according to the Cooper test:
A) "excellent";
B) "good";
C) "satisfactory";
D) "bad".
22. In well-trained athletes involved in sports requiring endurance, the heart rate (HR) at rest is often equal to:
A) 80 - 70 beats / min;
B) 70 - 60 beats / min;
B) 60 - 50 beats / min;
D) 40 beats / min and below.
23. Romberg's test determines a person's ability to maintain balance in the absence of correction by the visual analyzer. It:
A) test for coordination of movements;
B) test for kinesthetic sensitivity;
C) test for proprioceptive sensitivity;
D) study of the functional capabilities of the neuromuscular apparatus.
24. The human heart consists of:
A) four sections: two ventricles and two atria;
B) three sections: two ventricles and one atrium;
B) three sections: one ventricle and three atria;
D) two sections: one ventricle and one atrium.
25. Ideally "clean" in sanitary and hygienic terms, dietary food products include the following culture:
A) buckwheat;
26. What is not part of a healthy lifestyle:
A) hiking trips;
B) compliance with the rules of hygiene;
C) sports entertainment;
D) unlimited TV viewing.
27. The most common means of developing endurance is:
A) sprinting, gymnastic exercises
B) throwing the ball, long jump
V) long running, skiing, swimming
D) morning hygienic gymnastics
28. The hardening of the lens of the eye is called presbyopia.
29. The ability to overcome external resistance or to counteract it through muscular efforts is called force.
30. A type of luge is called skeleton.
31. The impact on the human body of an external factor that violates the structure and integrity of tissue, and the normal course of physiological processes is called injury.
32. The pushing apparatus in athletics is called core.
33. The volleyball court divider is called net.
34. The uniform of a sports team is called the form.
35. Items that protect the shins of football players and hockey players are called shields.
Fatigue is a temporary decrease in performance under the influence of prolonged exposure to stress. It arises as a result of the depletion of the internal resources of the individual and the mismatch in the work of the systems that support the activity.
Fatigue has various manifestations on the behavioral (decrease in labor productivity, decrease in the speed and accuracy of work), physiological (difficulty in developing conditioned connections, increased inertia in the dynamics of nervous processes), psychological (decreased sensitivity, impaired attention, memory, intellectual processes, shifts in emotional motivational levels, accompanied by the formation of a complex of subjective experiences of fatigue.The specificity of manifestations of fatigue depends on the type of load, the localization of its impact, the time required to restore the optimal level of performance.
Fatigue, a set of changes in the physical and mental state of a person and an animal, developing as a result of activity and leading to a temporary decrease in its effectiveness. The subjective feeling of fatigue is called fatigue.
The dynamics of fatigue
The dynamics of working capacity includes phases: mobilization, i.e. preparation for activity, a primary reaction reflecting the process of quantitative balancing, hypercompensation, i.e. search for an optimal solution, compensation, when the working capacity is adequate to the requirements of the activity, subcompensation, decompensation and breakdown, reflecting the gradual depletion of the body's reserves and a decrease in working capacity. U. is characteristic of all phases, starting with subcompensation, when there is a significant reduction in physiological reserves and the body switches to energetically less favorable types of reactions, for example, maintaining the minute volume of blood flow by increasing the frequency of heart contractions instead of a more favorable reaction of increasing the stroke volume; the implementation of a motor reaction by a large number of functional muscle units with a weakening of the force of contractions of individual muscle fibers, i.e. violation of the alternation of periods of work and rest of the muscle groups involved in the contraction. In a person in the initial stages of U., the effectiveness of activity decreases, i.e. the amount of physiological and mental costs required for one and the same labor act increases; then labor productivity also falls. With fatigue, first of all, the stability of the autonomic functions, the strength and speed of muscle contraction are disturbed, the regulation of functions, the development and inhibition of conditioned reflexes deteriorate. As a result, the pace of work slows down, the rhythm, accuracy and coordination of movements are disturbed, for the same activity, large energy costs are required. The thresholds of sensory (sensitive) systems rise, stereotypical forms dominate in decision-making processes, attention is weakened and it is difficult to switch. Fatigue is characterized by an increase in the number of errors and a change in their structure: in the initial phases, quantitative errors dominate, in subsequent phases, qualitative ones appear. The development of the picture of fatigue can be generally characterized as a violation of the adequacy of the body's response to the requirements imposed by the nature of the activity. At the same time, all 3 basic requirements of adequacy are violated: the optimality of the particular reactions that underlie the activity and their coordination with each other, the qualitative and quantitative correspondence of the body's response to the requirements of the task and the minimization of the consumption of physiological reserves.
With pronounced fatigue, there is a complete cessation of work. Subjective signs of human fatigue - unpleasant sensations in working muscles and joints, with a static posture - pain and a feeling of swelling in the muscles of the back, abdomen and neck, the appearance of pain in the forehead and the back of the head, especially with sensory and mental fatigue, impaired concentration, easy distraction, at first some increase, and then a sharp limitation of contacts with others, an unconscious desire to make breaks from work more frequent and longer. Fatigue in animals and humans has a number of common mechanisms associated with biochemical changes at the cellular level and impaired conditioned reflex activity. However, both the dynamics and a number of structural mechanisms of fatigue, determined in humans by the regulating role of the motives of activity, its goals and social nature, make it possible to detect a number of fundamental differences in fatigue in animals and humans. In particular, in animals there is no strict development of the phases of fatigue, a sequential decrease in quantitative indicators is more characteristic, a change in the structure of activity is less pronounced, fatigue is practically not suppressed by volitional effort.
The dynamics of fatigue is influenced by the nature of the activity, primarily its intensity, extensiveness and pace. There is an optimal intensity of activity in which fatigue occurs later; an increase or decrease in this intensity accelerates the onset of fatigue. Fatigue develops rapidly during monotonous, static and sensory depletion of activity. So, during activities during which a person performs the same working operation for a long time, requiring a limited set of movements, for example, during highly specialized work on an assembly line (monotonous activity), attention decreases, positive motives of activity fade away and fatigue develops quickly. Fatigue appears especially early in those cases when work is performed with a fixed tense posture (static activity) or when the flow of stimuli arriving at a person is limited, for example, sound or light signals containing information about the conditions of activity. Of the external factors of the working environment, the microclimate is of great importance, especially temperature, humidity and air velocity, air composition and the presence of chemical impurities in it, noise, vibration, illumination, etc. The development of fatigue depends on the state of health and physical fitness of a person, which not only determine large physiological reserves, but also contribute to a faster and more stable mobilization and formation of functional systems. The rate of emergence and development of U. also depends on a number of psychological characteristics of the personality - the level of anxiety, volitional qualities, including persistence, and other activation parameters, i.e. such functional properties of a person, which provide the degree of realization in a specific activity of his potential. For example, attention as an activation parameter provides great opportunities for memorization, and a high level of volitional qualities allows you to maintain the required level of activity with a pronounced feeling of fatigue. The leading role belongs to the highest mental characteristics - ideals and worldview.
Types of fatigue
Depending on the type of work performed, mental and physical fatigue is distinguished, in which deviations of energy metabolic parameters are taken into account, for example, changes in body temperature, bioelectric potentials. Due to the fact that the fundamental commonality of physical and mental fatigue has been revealed, a classification based on the predominant localization of fatigue in the links of the nervous system that ensures human activity is becoming widespread. Thus, sensory fatigue and its varieties (perceptual and informational) and effector fatigue are distinguished. In addition, general fatigue is distinguished as a generalized form. However, this or that classification depends on the accepted physiological theory of fatigue. Sensory fatigue develops as a result of prolonged or intense exposure to a stimulus (for example, loud noise, light), in which primary changes occur in sensory systems, from the receptor to the cortical end of the analyzer. Perceptual fatigue, localized mainly in the cortical end of the analyzer, is associated with the difficulty of detecting a signal (for example, with large noise, with its low intensity, difficulty in differentiation). Information fatigue develops as a result of insufficient information or during information overload, when the greatest load falls on the dynamics of intercentral relations, which consists in closing temporary connections between various structures in the central nervous system and revitalizing associative connections, which make it possible to correctly reflect the objective picture of the external environment in consciousness. Effective fatigue occurs when changes are localized mainly in the parts of the central nervous system that form the motor act. With changes that appear as a result of intensive processes of reproductive activity, associated only with the processing of the information received according to strict rules (for example, counting, categorization by headings), as well as productive, including the processes of converting information and forming judgments, concepts, inferences, etc., and heuristic, i.e. creative, carried out according to individual, implicit algorithms, mental fatigue is formed. Due to the fact that during work, all of the listed changes are often combined, general fatigue is highlighted, while emphasizing the most pronounced disorders in the central nervous system.